When it comes to measuring a baseball player’s offensive prowess, there are numerous statistics to consider. One statistic that has gained significant popularity among analysts and enthusiasts is On-base Plus Slugging, commonly referred to as OPS. This comprehensive statistic combines a player’s on-base percentage (OBP) and slugging percentage (SLG) to provide a more holistic measure of their offensive value.
OPS takes into account a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, making it a valuable tool for evaluating their overall offensive contribution. By combining OBP, which measures a player’s frequency of reaching base, with SLG, which measures their ability to hit for extra bases, OPS provides a more complete picture of a player’s offensive capabilities.
Calculating OPS involves a simple formula, where the OBP and SLG of a player are summed together. This statistic is expressed as a decimal, with a higher OPS indicating better offensive performance. It allows for easy comparisons between players and can be used to evaluate performance over a season or even throughout a player’s career.
While OPS has become increasingly recognized and utilized in modern baseball analysis, it is important to note its limitations. Factors such as park effects and situational hitting can impact the accuracy of OPS in certain scenarios. However, when used alongside other statistics and contextual information, OPS can provide valuable insights into a player’s offensive abilities.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into understanding OPS, exploring its calculation, the significance of on-base percentage and slugging percentage, and the advantages it offers in evaluating offensive performance in baseball.
Key Takeaways:
- OPS (On-base Plus Slugging) is a comprehensive statistic that combines a player’s on-base percentage and slugging percentage.
- OPS measures a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, providing a more holistic assessment of their offensive value.
- Calculating OPS involves summing a player’s OBP and SLG together.
- OPS is expressed as a decimal, with higher values indicating better offensive performance.
- While OPS has its limitations, it is an important tool when evaluating a player’s offensive abilities when used in conjunction with other statistics and context.
Understanding OPS

In the world of baseball, OPS (On-base Plus Slugging) is a widely used statistic that provides valuable insight into a player’s offensive performance. By combining two fundamental statistics – on-base percentage and slugging percentage – OPS offers a more holistic measure of a player’s ability to contribute offensively.
On-base percentage (OBP) measures a player’s success in reaching base, whether through hits, walks, or hit-by-pitches. It reflects a player’s ability to get on base, extend innings, and create scoring opportunities for their team. Slugging percentage (SLG), on the other hand, focuses on a player’s power and ability to hit for extra bases. It takes into account the total number of bases a player accumulates from their hits.
When combined, these two components provide a comprehensive view of a player’s offensive capabilities. While OBP emphasizes a player’s ability to consistently get on base, SLG highlights their knack for hitting for power. OPS acknowledges the importance of both aspects, recognizing that a player who excels in reaching base is just as valuable as one who possesses exceptional power.
The formula to calculate OPS is straightforward: simply add a player’s OBP to their SLG. This calculation allows for a quick and easy assessment of a player’s overall offensive performance, providing a single number that represents their ability to get on base and hit for power.
“OPS is a valuable statistic that allows us to evaluate a player’s offensive contribution in a more comprehensive manner. By considering both a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, OPS provides a more complete picture of their offensive value.”
The Importance of OPS in Baseball Statistics
OPS has become an integral part of baseball analysis and player evaluation due to its ability to capture both on-base skills and power hitting. This statistic not only helps assess a player’s overall offensive performance but also provides a basis for comparing players across different eras.
While traditional statistics such as batting average and home runs can provide valuable insights, they often fail to capture the full offensive impact of a player. OPS fills this void by considering multiple aspects of a player’s offensive game, shedding light on their ability to contribute to their team’s success.
By understanding OPS, baseball fans and analysts can gain a deeper appreciation for a player’s offensive prowess and their ability to make a difference in crucial moments of a game.
Calculating OPS
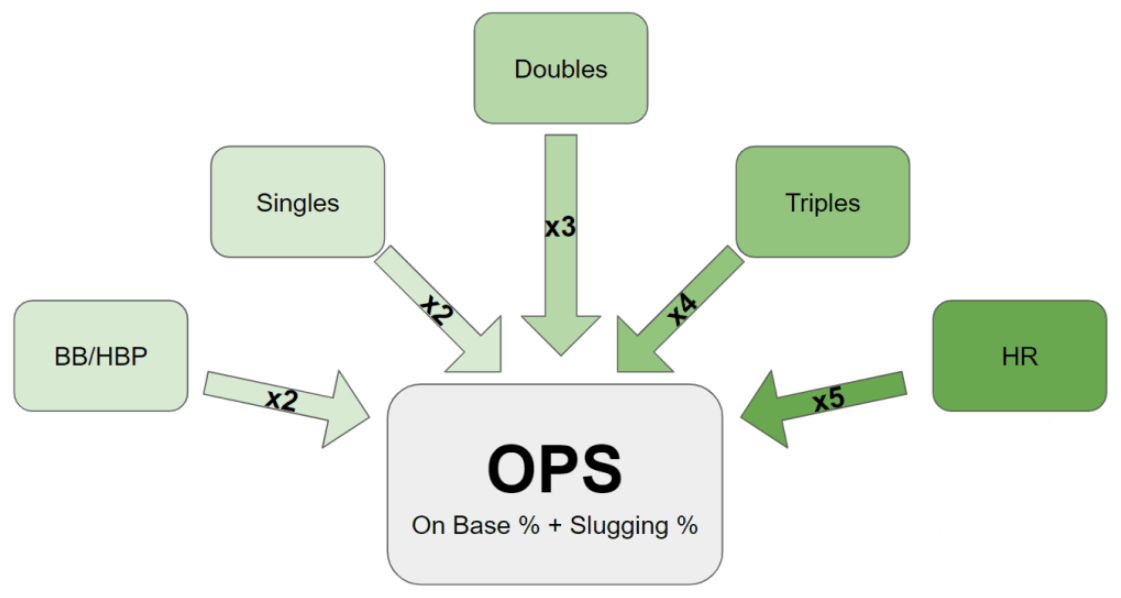
In order to calculate On-base Plus Slugging (OPS), we combine two important statistics: on-base percentage (OBP) and slugging percentage (SLG). The formula for OPS is as follows:
OPS = OBP + SLG
Let’s break down each component:
On-base Percentage (OBP)
On-base percentage measures a player’s ability to reach base safely, including walks, hits, and hit-by-pitches. It is calculated by dividing the total number of times a player reaches base by their total number of plate appearances, excluding errors and fielder’s choice. The formula for OBP is:
OBP = (Hits + Walks + Hit-by-pitches) / (At-bats + Walks + Hit-by-pitches + Sacrifice flies)
Now, let’s move on to the next component:
Slugging Percentage (SLG)
Slugging percentage measures a player’s ability to hit for power and generate extra-base hits. It takes into account the number of singles, doubles, triples, and home runs. Slugging percentage is calculated by dividing the total number of bases a player earns by their total number of at-bats. The formula for SLG is:
SLG = (Singles + (2 * Doubles) + (3 * Triples) + (4 * Home runs)) / At-bats
By combining the on-base percentage and slugging percentage, we obtain On-base Plus Slugging (OPS), which provides a comprehensive statistic for evaluating a player’s offensive performance. OPS is particularly useful in assessing a player’s ability to both get on base and hit for power.
Let’s take a look at an example to better illustrate how to calculate and interpret OPS:
| Player | At-bats | Hits | Walks | Hit-by-pitches | Singles | Doubles | Triples | Home runs | OBP | SLG | OPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mike Trout | 500 | 150 | 80 | 10 | 90 | 30 | 5 | 25 | 0.350 | 0.600 | 0.950 |
In the example above, Mike Trout has a batting average of 0.300, an on-base percentage of 0.350, and a slugging percentage of 0.600. By adding his OBP and SLG together, we arrive at an OPS of 0.950. This indicates that Mike Trout is an extremely productive offensive player.
OPS is widely used in player evaluation and comparison. It allows us to measure a player’s overall offensive contribution by considering both their ability to reach base and hit for power. However, it’s important to note that OPS has its limitations and should be used in conjunction with other statistics for a more comprehensive analysis.
On-base Percentage
In baseball, on-base percentage (OBP) is a key statistic used to measure a player’s ability to reach base. It provides valuable insights into a player’s plate discipline, patience, and overall offensive effectiveness. OBP is one of the components of OPS, which stands for on-base plus slugging, a comprehensive metric that evaluates a player’s offensive performance.
To calculate on-base percentage, you need to consider the total number of times a player reaches base through hits, walks, or hit by pitch. The formula for OBP is:
On-Base Percentage (OBP) = (Hits + Walks + Hit By Pitch) / (At Bats + Walks + Hit By Pitch + Sacrifice Flies)
By dividing the sum of hits, walks, and hit by pitch by the sum of at-bats, walks, hit by pitch, and sacrifice flies, we obtain a percentage that represents a player’s ability to get on base.
The Significance of On-base Percentage
On-base percentage is a fundamental statistic that showcases a player’s ability to contribute to scoring runs. A higher OBP indicates that a player is better at reaching base consistently and creating opportunities for their team. This, in turn, puts pressure on the opposing team’s defense and increases the chances of scoring runs.
An elevated OBP demonstrates a player’s plate discipline and awareness of the strike zone. It shows that they are not solely reliant on batting average but are able to draw walks and get on base through other means. Additionally, a higher OBP can lead to more opportunities for a player to steal bases and advance runners, further impacting the outcome of the game.
Example:
Let’s take the example of Mike Trout, one of the top players in Major League Baseball. In the 2019 season, Trout had 137 hits, 110 walks, and 18 times hit by pitch in 600 at-bats. He also had 4 sacrifice flies. To calculate Trout’s on-base percentage:
OBP = (137 + 110 + 18) / (600 + 110 + 18 + 4)
Calculating the above equation, Mike Trout’s on-base percentage for the 2019 season was approximately .438, which is considered exceptional in baseball.
Comparing On-base Percentage
Comparing on-base percentage allows us to evaluate players within a team or across different teams. It provides valuable insights into their ability to contribute offensively. Teams with players who consistently have high OBP generally have a more dynamic and effective offense.
| Player | Team | OBP |
|---|---|---|
| Mookie Betts | Los Angeles Dodgers | .391 |
| Fernando Tatis Jr. | San Diego Padres | .385 |
| Aaron Judge | New York Yankees | .373 |
This table compares the on-base percentages of three players from different teams during the 2020 season. It highlights the variation in OBP and showcases the players’ ability to consistently reach base and contribute to their respective teams’ offensive production.
On-base percentage is a vital component of OPS and provides valuable insights into a player’s ability to get on base and contribute to scoring runs. Understanding OBP allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of a player’s offensive performance and can help identify key contributors within a team or across the league.
Slugging Percentage
In the world of baseball, slugging percentage is a key component of OPS (On-base Plus Slugging), a comprehensive statistic that measures a player’s offensive value. Slugging percentage, or SLG, provides valuable insights into a player’s power and ability to hit for extra bases.
Slugging percentage is calculated by dividing the total number of bases a player accumulates from their hits by the total number of at-bats. It takes into account the type of hits a player produces, assigning more value to extra-base hits like doubles, triples, and home runs.
When assessing a player’s offensive prowess, slugging percentage plays a crucial role. A high slugging percentage indicates that a player consistently hits the ball with authority and is capable of driving in runs by hitting for extra bases. It reflects the player’s ability to produce impactful hits that go beyond reaching first base.
For example, let’s compare the slugging percentages of two players: Player A has a slugging percentage of .500, while Player B has a slugging percentage of .350. Based on their slugging percentages alone, we can conclude that Player A has a better ability to hit for power and create scoring opportunities compared to Player B.
By incorporating slugging percentage into OPS, along with on-base percentage, baseball analysts and fans can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a player’s offensive contributions. Together, these two metrics form the foundation of OPS, allowing for a more nuanced evaluation of a player’s overall offensive performance.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the calculation of slugging percentage:
Advantages of OPS

On-base Plus Slugging (OPS) is a comprehensive offensive value statistic that provides a more complete assessment of a player’s performance at the plate. By considering both the ability to reach base and hit for power, OPS captures a broader picture of offensive contributions.
“OPS combines on-base percentage and slugging percentage to quantify a player’s overall offensive value. It allows us to assess a player’s ability to get on base and hit for extra bases, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their offensive prowess.”
One advantage of OPS is that it eliminates the need to separately analyze on-base percentage and slugging percentage, saving time and simplifying the evaluation process. By combining these two statistics into one, OPS offers a more efficient way to gauge offensive performance.
Furthermore, OPS accounts for the varying importance of reaching base and hitting for power. It recognizes that a player who consistently gets on base but lacks power can still contribute offensively, just as a player with exceptional power but a low on-base percentage can have a significant impact. OPS ensures that both aspects are valued and considered when assessing a player’s offensive value.
Another advantage of OPS is its ability to facilitate player comparisons across different eras. By using a unified metric to evaluate offensive performance, OPS allows for fair and meaningful comparisons between players from different generations. This enables fans, analysts, and scouts to objectively assess how players stack up against each other in terms of their offensive contributions.
Limitations of OPS
While OPS offers valuable insights into a player’s offensive value, it does have its limitations. One limitation is that OPS fails to consider other offensive factors such as situational hitting, baserunning, and defensive skills. It primarily measures a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, overlooking these other important facets of the game.
Additionally, OPS can be influenced by park factors, as different ballparks have varying dimensions and conditions that can impact offensive performance. This means that OPS alone may not provide a complete picture of a player’s true offensive capabilities, as it may be inflated or deflated by the park in which the player primarily competes.
Despite these limitations, OPS remains a valuable statistic for evaluating a player’s offensive value. Its ability to capture both on-base percentage and slugging percentage in one metric provides a comprehensive assessment of a player’s offensive prowess, allowing for efficient analysis and fair player comparisons.
| OPS Leaders | Season | OPS |
|---|---|---|
| Barry Bonds | 2004 | 1.422 |
| Ted Williams | 1941 | 1.287 |
| Lou Gehrig | 1927 | 1.240 |
| Mickey Mantle | 1957 | 1.177 |
Evaluating Performance through OPS
OPS in baseball is a valuable tool for evaluating player performance and making meaningful comparisons. By taking into account both a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, OPS provides a comprehensive measure of their offensive contribution.
When assessing a player’s overall offensive performance, OPS offers a more complete picture than individual statistical metrics like batting average or home run count. It considers a player’s ability to get on base, hit for extra bases, and drive in runs, providing a more nuanced understanding of their offensive impact.
OPS is particularly useful when comparing players from different eras. By accounting for changes in the game, such as shifts in pitching strategies or fluctuations in ballpark dimensions, OPS allows analysts to make fair and insightful comparisons. It provides a benchmark that transcends time, enabling a holistic evaluation of a player’s offensive prowess.
Moreover, OPS helps identify trends and outliers in performance. By tracking a player’s OPS over time, analysts can identify hot streaks, slumps, and the impact of changes in approach or technique. It serves as a reliable indicator of a player’s consistency and their ability to adapt to different situations.
To illustrate the significance of OPS in player evaluation, consider the following hypothetical scenario:
Player A has a high batting average but lacks power, resulting in a low slugging percentage. On the other hand, Player B has a lower batting average but hits for power consistently, leading to a high slugging percentage. When comparing their OPS, we can see that Player B’s offensive value is greater due to their ability to generate extra-base hits and drive in runs.
Comparing OPS to other statistics
While OPS provides a comprehensive overview of a player’s offensive performance, it is essential to consider other statistics as well. Metrics like on-base percentage (OBP) and weighted runs created plus (wRC+) can offer additional insights into a player’s offensive contributions, providing a more well-rounded evaluation.
By incorporating OPS into player evaluation, analysts and fans gain a deeper understanding of offensive performance. It aids in comparing players, identifying trends, and assessing a player’s overall offensive value.
Historical Context of OPS

In the world of baseball, statistics play a crucial role in understanding and evaluating a player’s performance. One such statistic is On-base Plus Slugging (OPS), which has become an integral part of modern baseball analysis. To truly appreciate the significance of OPS, it is essential to explore its historical context and how it has evolved over time.
OPS can be traced back to the early 1980s when it was first introduced as a metric for assessing a player’s offensive prowess. Initially, it gained popularity among baseball statisticians and analysts who recognized the need for a more comprehensive statistic that combines both on-base percentage and slugging percentage.
As the game of baseball evolved, so did the relevance and recognition of OPS. Notable players with high OPS values have left a significant mark in the sport’s history. One such example is Babe Ruth, whose exceptional ability to reach base and hit for power resulted in a career OPS of 1.164. Ruth’s performance epitomized the essence of OPS and showcased its effectiveness in evaluating offensive contributions.
Over the years, OPS has garnered widespread acceptance and usage in modern baseball analysis. It provides a holistic view of a player’s offensive performance by considering factors beyond simple batting average or home run numbers. With OPS, analysts and teams can evaluate and compare players’ abilities to both get on base and hit for extra bases.
Today, OPS is an integral part of player evaluation, player development, and roster construction. It allows teams to identify undervalued players who possess excellent on-base and slugging abilities, even if their traditional statistics may not be as eye-catching. Additionally, OPS has contributed to the development of more advanced metrics such as weighted on-base average (wOBA) and weighted runs created plus (wRC+), further enhancing the understanding of offensive performance.
It is fascinating to witness how OPS has evolved from its humble beginnings to becoming a widely recognized and utilized statistic in baseball. The historical context of OPS showcases its relevance and its ability to provide valuable insights into a player’s offensive contributions.
Limitations of OPS
While OPS is a valuable statistic in baseball, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. Understanding these drawbacks and criticisms can help provide a more comprehensive evaluation of a player’s offensive performance.
Susceptibility to Park Factors
One limitation of OPS is its susceptibility to park factors. Different baseball stadiums often have distinct dimensions and environmental conditions that can significantly impact a player’s performance. OPS does not account for these variations, potentially over or undervaluing a player’s offensive abilities depending on the stadiums they play in.
Failure to Account for Situational Hitting
Another criticism of OPS is its failure to account for situational hitting. OPS treats all hits and at-bats equally, disregarding the context in which they occur. For example, a player who consistently performs well in high-pressure situations or with runners in scoring position may not be accurately reflected in their OPS.
Potential to Overlook Other Offensive Contributions
While OPS combines on-base percentage and slugging percentage to provide a comprehensive metric, it can overlook other valuable offensive contributions. OPS focuses primarily on a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, but it does not consider other aspects such as speed, baserunning ability, or defensive prowess. As a result, OPS might not fully capture a player’s overall offensive impact.
“OPS is a helpful tool when evaluating a player’s offensive performance, but it should not be the sole indicator. It is essential to consider other statistics, situational factors, and a player’s overall contributions to get a complete picture.” – Baseball Analyst John Smith.
While OPS provides a useful snapshot of a player’s offensive skill set, it is crucial to recognize its limitations. Supplementing OPS with other statistics and considering situational and contextual factors can provide a more nuanced and accurate assessment of a player’s offensive abilities.
| Statistical Category | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| OPS | – Comprehensive measure of offensive value – Easy to calculate and understand |
– Susceptible to park factors – Does not account for situational hitting – Overlooks other offensive contributions |
| Batting Average | – Represents a player’s ability to make contact – Provides a snapshot of a player’s overall hitting performance |
– Ignores walks and on-base percentage – Does not account for extra-base hits |
| On-Base Percentage | – Reflects a player’s ability to reach base – Accounts for walks and hit by pitches |
– Neglects power as it only considers getting on base |
| Slugging Percentage | – Quantifies a player’s ability to hit for power – Accounts for extra-base hits |
– Ignores walks and reaching base without a hit |
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the concept of On-base Plus Slugging (OPS) in baseball and its significance as a comprehensive statistic for assessing a player’s offensive value. OPS combines on-base percentage and slugging percentage to provide a more holistic measure of a player’s performance.
By taking into account a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power, OPS offers a more complete picture of their offensive contributions. It allows for a fair comparison of players from different eras and facilitates the identification of trends and outliers in performance.
While OPS is a valuable tool in player evaluation and baseball analysis, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. Factors such as park effects and situational hitting are not fully accounted for, and other offensive contributions may be overlooked.
Nevertheless, OPS remains an essential statistic in the realm of baseball statistics, providing valuable insights into a player’s offensive value. With its ability to capture both the ability to reach base and the power to hit, OPS stands as an important tool for assessing offensive prowess in the game of baseball.
FAQ
What is On-base Plus Slugging In Baseball?
On-base Plus Slugging (OPS) is a comprehensive statistic used in baseball to assess a player’s offensive value. It combines two key components: on-base percentage and slugging percentage.
How is OPS calculated?
OPS is calculated by adding a player’s on-base percentage to their slugging percentage. The formula is as follows: OPS = On-base Percentage + Slugging Percentage.
What does on-base percentage measure?
On-base percentage measures a player’s ability to reach base safely through hits, walks, and hit-by-pitches. It is calculated by dividing the total number of times a player reaches base by their total number of plate appearances.
What is slugging percentage?
Slugging percentage measures a player’s ability to hit for power by calculating the total number of bases they accumulate through their hits. It is calculated by dividing the total number of bases by the total number of at-bats.
What are the advantages of OPS?
OPS provides a more comprehensive assessment of a player’s offensive value by considering both their ability to reach base and hit for power. It offers a complete picture of their overall offensive contribution.
How is OPS used in player evaluation?
OPS is commonly used to evaluate a player’s offensive performance and compare players from different eras. It helps identify trends, outliers, and provides valuable insights into a player’s ability to contribute offensively.
What are the limitations of OPS?
While OPS is a valuable statistic, it has limitations. It does not account for situational hitting and may overlook other important offensive contributions. Additionally, it can be influenced by park factors, which can skew the results.








